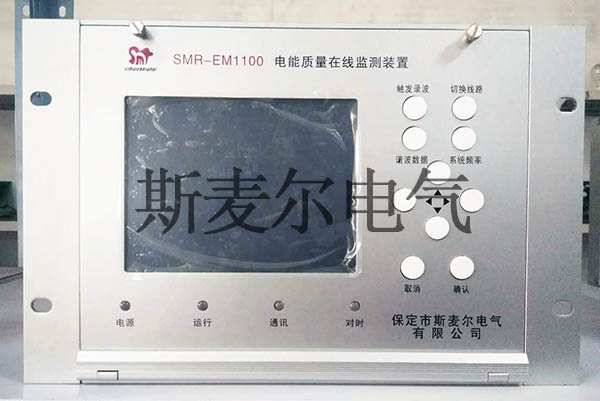
Online temperature measurement device for electrical contacts main components
Release time:
2025-02-27
Temperature Sensor: Responsible for collecting temperature data from electrical contacts. Common types of temperature sensors include battery-powered wireless temperature sensors and CT induction power wireless temperature sensors. These sensors have characteristics such as high precision, high sensitivity, and strong anti-interference ability, ensuring that the collected temperature data is accurate.
Temperature Sensor: Responsible for collecting temperature data from electrical contacts. Common types of temperature sensors include battery-powered wireless temperature sensors and CT induction power wireless temperature sensors. These sensors feature high precision, high sensitivity, and strong anti-interference capabilities, ensuring that the collected temperature data is accurate.
Display Terminal: Used to display real-time temperature data from electrical contacts. The display terminal typically features a large LCD screen, Chinese menu, and easy operation, allowing users to intuitively view temperature data.
Monitoring System (if available): Centralizes the monitoring and management of temperature data from multiple electrical contacts. The monitoring system usually has functions such as data recording, historical data querying, and alarm notifications, facilitating remote monitoring and management of electrical equipment.
Keyword:
Recent information
The main factors of insufficient selection principle for small current grounding.